Reactive Solid-Phase Epitaxy: A Powerful Method for Layered Oxide Heteroepitaxy
[Adv. Funct. Mater. 2003/ Science 2003/ J. Appl. Phys. 2004/ Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2009/ Cryst. Growth Des. 2010]
The R-SPE procedure for the growth of single-crystalline InGaO3(ZnO)5 films is as follows.
Step 1: a ZnO epitaxial layer was grown on a (111)-YSZ substrate by PLD at 600oC. Thickness of the ZnO epitaxial layer was ~2 nm, evaluated by grazing incidence X-ray reflectivity (GIXR) measurements.
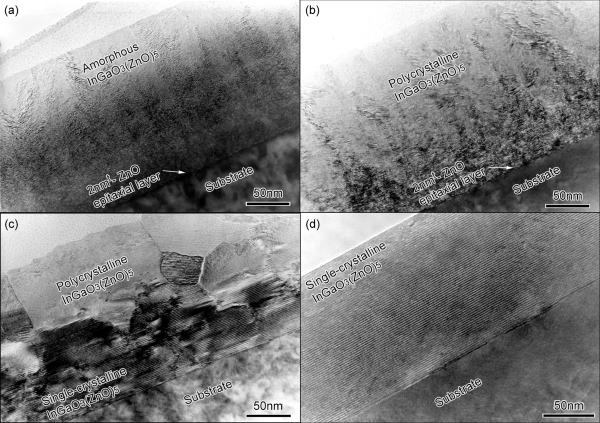
Step 2: a 150-nm-thick polycrystalline InGaO3(ZnO)5 film was deposited on the ZnO epitaxial layer at room temperature (25oC)(a). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) revealed that the chemical composition of the deposited InGaO3(ZnO)5 film differs insignificantly from that of the target.
Step 3: The resultant bilayer film was fully covered by placing a YSZ plate (10 mm x 10 mm x 0.5 mm) on the film surface to suppress vaporization of ZnO and In2O3 during the annealing in step 4.
Step 4: The bilayer film was annealed at 1400oC for 0.5 h in air (d). [(b) 800oC, (c)1000oC]
Step 5: The film was cooled down to room temperature in the furnace. Finally, a YSZ cap plate was removed and the surface of the annealed film looks very clean without chemical reaction with the YSZ plate.